Empathize
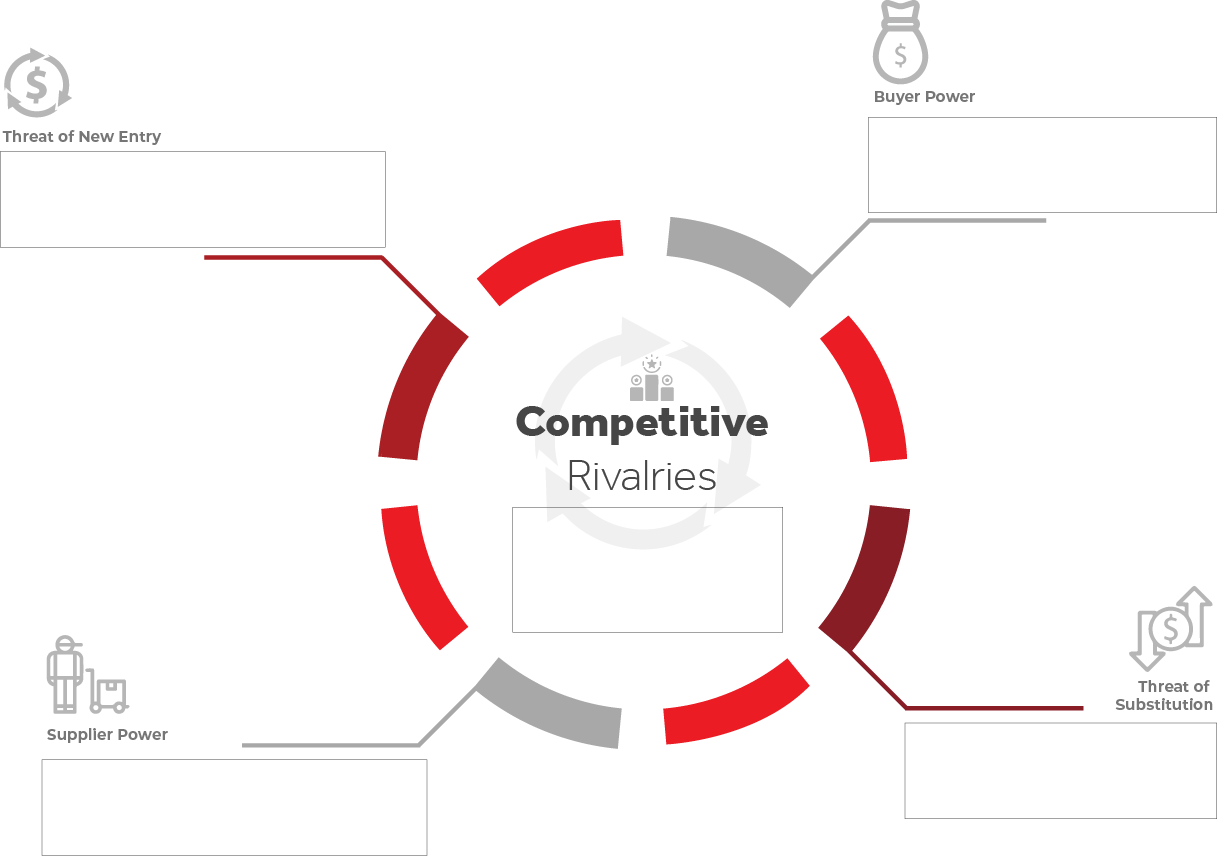
Porter’s Five Forces
Why Use this tool ?
Spot risks, challenges and opportunities
Porter’s Five Forces gives you a structured way to analyze your competitive environment. It helps you understand which pressures are strongest, where your vulnerabilities lie, and where opportunities might exist to shape a smarter long-term position.
what you should know
Start With: Industry research, market data, and team knowledge
End With: A shared view of competitive forces and how they affect your project
Time Needed: 30 – 60 minutes
Difficulty: ⭐ ⭐ ☆☆☆ (2 out of 5 – structure and analytical)
A quickguide to start
1. Introduce the tool. Explain that there are five main “forces” that shape competition in any industry: new players entering, substitutes, customer influence, supplier influence, and rivalry among competitors.
2. Look at each force. Go one by one and discuss what’s happening in your industry.
3.Discuss your position. For each force, note where your company is strong and where it may be vulnerable.
4. Spot implications. Highlight the biggest risks, opportunities, or warning signs that come out of the analysis.
5. Summarize. Agree on which forces matter most for your strategy and what actions you should watch or take next.
helpful tips
- Use this tool to assess the long-term appeal of your market, not just short-term events.
- Focus on structural forces (market conditions, not temporary fluctuations).
- Look for both threats and opportunities, some forces can be influenced or turned to your advantage.
Format summary
Threat of new entry
Think about how easy or hard it is for new companies to enter your market.
- Questions to ask: Who might enter? What would make it easy or difficult for them? How vulnerable is the industry to newcomers?
- What to note down: time and cost of entry, need for specialist knowledge, economies of scale, cost advantages of incumbents, technology protection, or legal/regulatory barriers.
Threat of substitution
Look at whether customers could switch to alternatives instead of using your product or service.
- Questions to ask: What other products or services could people use to meet the same need? How likely are they to switch?
- What to note down: quality and performance of substitutes, ease or cost of switching.
Buyer power
Consider how much influence customers have over what you sell and at what price.
- Questions to ask: How much control do customers have in setting prices or pushing for better quality/service? Can they easily move to a competitor?
- What to note down: number of customers, size of their orders, how they compare your product with competitors, price sensitivity, ability to substitute, and cost of switching.
Supplier power
Look at how much influence your suppliers have over your industry.
- Questions to ask: Are there only a few suppliers you depend on? How much can they raise costs, control quality, or limit availability?
- What to note down: number and size of suppliers, uniqueness of what they provide, ease of finding substitutes, and cost of switching suppliers.
Competitive rivalries
Focus on the level and nature of competition among existing players.
- Questions to ask: How many competitors are there? Do they compete mainly on price, technology, quality, or service? How fierce is the rivalry?
- What to note down: number of competitors, differences in quality or service, customer loyalty, switching costs, and what it would take for competitors to exit the market.
One-Liner Prompts for the Canvas
- Threat of New Entry → How easy is it for new players to enter the market?
- Threat of Substitution → What alternatives could customers switch to?
- Buyer Power → How much influence do customers have over price and choices?
- Supplier Power → How much control do suppliers have over costs and availability?
- Competitive Rivalries → How intense is the fight between existing competitors?
RACU meets AI
Porter’s Five Forces
How Can AI Make RACU Easier ?
AI can be your creative partner and research assistant, ready to help you move faster and think deeper at every step of the RACU process.
For each RACU tool, we’ll share a ready-to-use AI prompt. Just copy the prompt into your favorite AI tool (like ChatGPT or Copilot) and it will guide you through the method step by step.
No need to fill out a blank form, the prompt starts the conversation and adapts to your answers in real time.
PROMPT – COPILOT, CHAT GPT
You are an innovation and strategy assistant helping me complete a Porter’s Five Forces analysis for a project or industry.
Your role is to proactively suggest insights for each of the five forces, while asking me to validate, adjust, or add details.
The five forces are:
- Threat of New Entry
- Threat of Substitution
- Buyer Power
- Supplier Power
- Competitive Rivalries
🔰 Step 1 – Define the Focus
Start by asking me:
👉 “What company, product, or industry are we analyzing with Porter’s Five Forces?”
→ Use my answer as the anchor for all following suggestions.
🔎 Step 2 – Suggest and Validate Each Force
Work through the five forces one at a time. For each force:
- Suggest 3–5 short, concrete statements that may apply to this force.
- Include both questions to reflect on and indicators to look for (e.g., barriers to entry, price sensitivity, substitute performance).
- Present them in a clear bullet list or mini-table.
- Ask me:
👉 “Which of these seem most relevant? What should we adjust, remove, or add? Do you want to go deeper into this section, or should we move on to the next force?”
- After my response, summarize the finalized points for this force in 2–3 bullets.
- If I say “move on” or give no preference, close the section and introduce the next force by name.
👀 Step 3 – Connect the Dots
After all five forces are filled, help me reflect on:
- Which forces are strongest or most critical.
- Where risks, vulnerabilities, or opportunities lie.
- What the overall picture suggests about the attractiveness of the industry.
📌 Final Step – Deliverables
At the end, provide me with:
- A completed Porter’s Five Forces table with all five sections summarized.
- A short summary of key risks, opportunities, and implications.
- A list of key references or sources with working links you used to generate ideas (reports, articles, datasets, or industry knowledge). Keep it concise but clickable so I can explore further.
⚡️ Important for You (the AI):
- Be proactive — don’t wait for me to provide everything; suggest strong starting points.
- Stay on one force at a time. Only move forward when I confirm.
- Always ask if I want to go deeper or move on — never assume I know how to continue.
- Summarize before moving on so each force feels “closed.”
- Keep statements short, clear, and scannable.
- Adapt everything to the company/product/industry I defined in Step 1.
- Always include sources with links in the Final Step.